Intro and Working of Roof
- Mar 28, 2025
- 10 min read
Intro to Roofing: Chapter 1
Introduction
By the end of this module, you should be able to describe the following:
What a roof is,
The history of a roof,
Responsibilities of a roofer,
Types of roofs, and
The importance of Roofs. Skip to quiz!
Roof
A roof is a top covering of a building, including all materials and structures necessary to support it on its walls. It protects us against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind.
A man needs shelter and protection from various elements. Throughout history, man has made roofs from available resources. People who lived in caves covered their structures with sod roofs made of soil and plants.
Sod roofs were good insulation but were not waterproof. People used earthenware roof tiles in Greece and Babylon between 4,000 and 5,000 years ago. In 100 BC, the Romans took variations of the Greek clay tiles to England.
5,000 years ago, Research showed the Chinese were the first to use glazed clay roof tile. Around 735 AD, thatched roofs were formed and used. After 300 years, Wood shingles were introduced.
In the 12th century in London, King John issued a law to replace thatch roofs with clay tiles to prevent spreading fire. In the 19th century, clay roofing tiles were produced in industries and became widely used.

In the past 200 years, there have been most evolutions in roofing materials. People still use the most available materials for their respective regions.
In the Southern part of North America, Wood and metal are used.
In the Northeast, Slate is used.
In the Midwest, Wood is used, and
In the Southwestern part of North America, tile is used.
We see technological advancements in glass, polymer, and smog-absorbing tiles. With a trend in energy savings, we may see an emergence in eco-friendly rooftop materials. Let’s learn about a day in the life of a roofer.
You’ll work at heights with tools like nail guns. You’ll have to climb up ladders quickly, precisely carrying shingles. It's hard because you would work directly in the sun in hot conditions.
You’ll have to head up and down the ladder throughout the day, as the installation process is repetitive and physical. Apart from work, you’ll spend a lot of time receiving training about safety and roofing techniques.
The roofers primarily focus on roof construction and repairs in the residential or commercial sectors. You must manage the installation or repair process and ensure that the roof is completed precisely according to State and city codes and manufacturer's specifications.
If you are a supervisor or team leader, you might attend sales and ownership meetings and walk the customer through the finished roof.
Roof Types
There are many different types of roofs, but 3 of them are the most commonly used.
They are:
Flat Roofs,
Gable Roofs, and
Hip Roofs.
Let’s learn about these roofs soon.
A flat roof is at an almost horizontal level. A roofer should avoid a perfectly flat roof and provide a slight slope to drain off the water. Flat roofs are mainly used on commercial properties, but some use them in residential spaces.
The advantages of flat roofs are:
They are less expensive than other roofs, as they use less material,
They are easy to install, and
They are easy to maintain and inspect.

Agable roof is a standard shape found in cold or temperate climates, which contains two sloped sides and meets at a ridge. The slopes form triangular extensions on two sides. bIt is constructed using rafters, trusses, or purlins.
A gable roof’s pitch can vary depending on the requirement. Also, the gutters are fitted on two sides of the roof, known as the Eave. You may see the different steepness’ shown in the image on the right.
Ridge is the peak where the two slopes of the roof meet. Pitch is a roof's steepness, expressed as a ratio of height to the horizontal distance between the two walls. We will discuss these terms in the next module.
The advantages of gable roofs are
They are easy to construct,
They form an ample amount of attic space, and
They allow efficient water drainage.
A hip roof is a type of roof that contains a downward slope on all sides of the walls, like a pyramid. There are no vertical sides on this type of roof, and the gutter is fixed on all sides of a hip roof. Unlike a gable roof, a hip roof has two triangular sides and two trapezoidal sides.
The advantages of hip roofs are:
They are good at resisting wind due to aerodynamics,
They can house wraparound gutters,
They are great at ventilation, and
They allow efficient water drainage.
Importance of Roofs
Let’s learn the importance of roofs. It is the most important element of a home that protects your potential client and their family from many weather conditions like sunlight, rain, hail, and snow. It also keeps the house warm in winter and keeps cool in summer.

The home can leak, decay, and experience other issues if a roof is in bad condition. A good roof may result in a good house value. If the roof contains algae or moss or looks weak, it shows that it wasn't taken care of by the owner, and the house's value falls.
A good roof adds value to the house through proper ventilation and attic insulation. The homeowner feels comfortable with the air conditioner at higher temperatures, and they might observe low heating and cooling bills.
In this module, you’ve learned about the following:
What a roof is?
History of a roof,
Responsibilities of a roofer,
Types of roofs, and
Importance of roof.
Working of Roof - Part 1
By the end of this module, you should be able to describe the following:
The function of a roof,
The components of the roof,
The purpose of each component on the roof, and
The terms used in Roofing. Skip to quiz!
Function of Roof
Let’s learn about the functions of the roof. A roof’s primary function is to enclose the house space and protect it from the effects of weather elements.
The roof is used to satisfy the following functions:
Insulation, and
Drainage.
Insulation: The roof provides insulation by maintaining warmth in the winter and cool in the summer. Roof insulation materials are usually installed under the roofing material.
With improper insulation, the roof can experience issues like ice formation near the eaves, also known as ice dams. The heat escaping from the top melts more ice, water collects at the bottom, and refreezes. Over time, this adds stress to the roof and can destroy the gutters.
Ice dams form on slope roofs of heated buildings in cold climat
es. They form when the accumulated snow melts due to heat, flows at the roof's bottom, and refreezes. Similarly, more water collects and leaks into the house after accumulation.
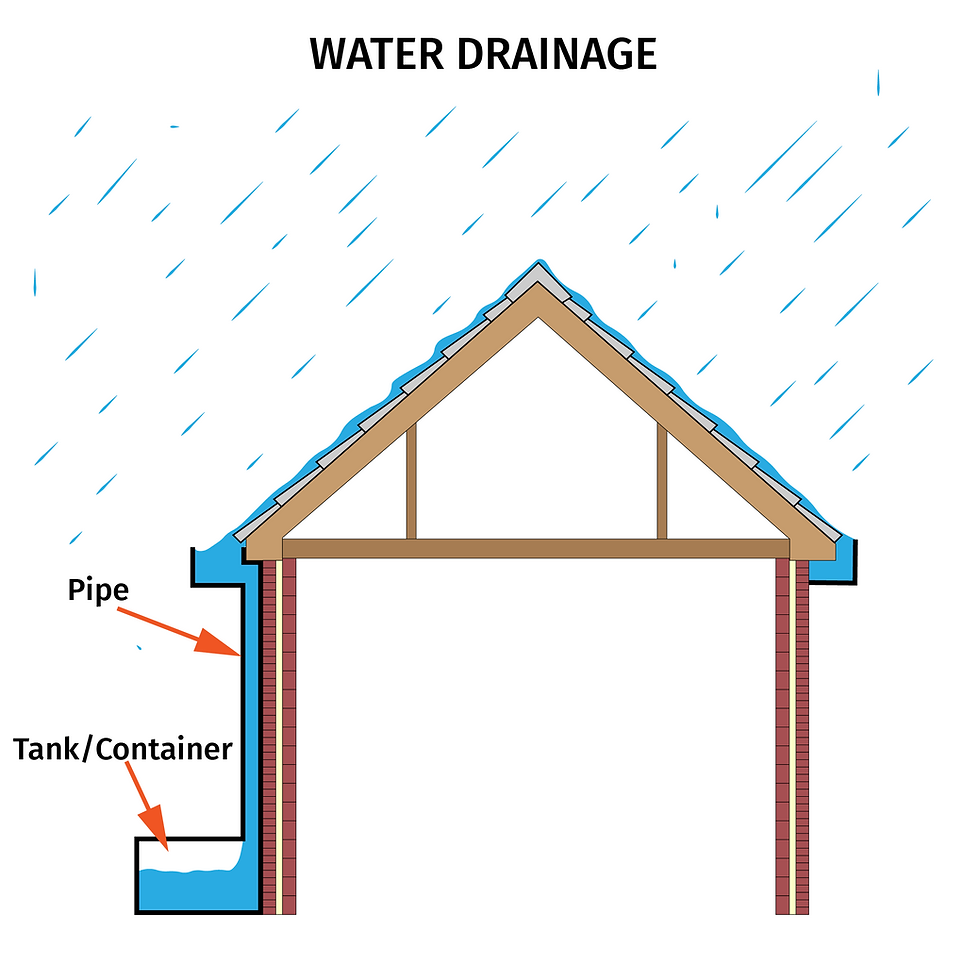
Drainage: The roof also provides shelter from water. During monsoons, water can damage property if not directed away from it. Thus, a drainage system helps collect water and transfer it to a container, after which the homeowner can use it.
In regions with heavy snowfall, it is beneficial to use metal roofing, as the smooth surface allows it to slide down as it gets heavier. Let’s learn about the components of a roof.
Components of Roof
The components used to form a roof are:
Leak Barrier,
Starter Strip Shingles,
Roof Deck Protection,
Shingles,
Ventilation, and
Ridge Cap Shingles.
Let’s learn about each of the components.
If you take a glimpse of the roof, it looks like a stack of shingles covering the house. They are more complicated than they look. Every roof layer has its importance, and they serve its purpose.
A leak barrier, also known as underlayment, creates a watertight seal that eliminates the threat of roof leaks at various spots that are:
Valleys,
Around chimneys,
Skylights,
Penetrations,
Roof slope transitions, and
Perimeter edges of the roof.
Leak barriers on the perimeter edges keep water from being absorbed into the roof deck, causing ice dams. The purpose of underlayment is to provide a layer of protection between shingles and the roof deck. It creates a flat, uniform surface for bonding shingles and keeps them from falling.
A starter strip shingle is a long, narrow asphalt shingle. It is installed along the roof's edge after the underlayment/leak barrier and before installing regular shingles. The purpose of the starter shingle is to bond with the shingles installed above it and seal them, preventing them from falling off.

It contains adhesives on them and helps bond the shingles with them. Next, we’ll learn about roof deck protection.
Roof deck protection is a layer that allows moisture to escape through the attic while providing firm layers of protection against wind-driven rain. It allows moisture to escape from your attic while providing a solid barrier against wind-driven rain.
Shingles are the most important layer of protection on the roof. They protect your home from the sun, water, and other weather conditions. They are small, rectangular-shaped pieces laid on the roof.
They are laid from bottom to top by overlapping the joints and are made of wood, slate, flagstone, metal, plastic, and composite materials like asphalt shingles. The granules are made of fiberglass, which protects the roof against fire.
Hot, moist air gets trapped underneath the roof. Ventilation helps this hot, moist air to escape outside the attic. Improper ventilation may lead to mold and damage the roof frame and deck.
Ridge Cap Shingles are installed on the ridge of a roof. It helps the heat and moisture in the attic to flow out from home and protects the house from leaks. Next, let’s learn about the few terms that are used in the roofing trade.
Terms Used in Roofing
Roofs come in various shapes and sizes, and you need to know some terms to describe the important features of a roof.
The terms used to describe a roof are:
Slope,
Eave,
Rake,
Gable,
Fascia,
Soffit,
Valleys,
Ridge, and
Hip.
Let’s learn about each of the terms. When a roof is inclined at some angle, it has a slope. It is also known as pitch. It is determined by rise over run.
Rise over Run is defined as the vertical rise in inches for every twelve inches of horizontal run. If a roof with 2 inches of rise for every 12 inches horizontally has a slope of 2/12, also known as a flat roof. Similarly, a roof with 4 inches of rise for every 12 inches horizontally has a slope of 4/12.
The standard roof slopes and the terms are as follows:
Flat Roof: 2/12
Low Slope: 2/12-4/12
Conventional Slope Roof: 4/12-9/12
Higher Slopes: 9/12 – 20/12
Steep Slope: 21/12 and higher.
You can see the pitch or steepness in the image on the right.

An eave is the roof's edge that extends beyond the face of the wall. During rain, the eave diverts rainwater from the walls and directs it to the ground. If there is a gutter, the water is directed into it. Eaves also cover the opening in the roof to allow for ventilation.
The rake is the exposed portion of a gable roof's sides that runs from the ridge to the eave of the sloped side. It protects the top edge of the roof, which is prone to leakage.
A Gable is a triangular section of the wall at the end of a pitched roof that extends from the peak to the eaves. A gable is only present in a gable roof.
Fascia is the vertical board under the roof’s eave. Usually, the gutter is installed on the fascia of the roof. If the fascia is not installed, the wooden areas may rot if they are continuously wet, which can sag and risk the structure's integrity.
A soffit is a horizontal board that connects the fascia and the wall. It is used to keep rainwater away from the rafter and trusses. If the soffit is not installed, the wooden areas may rot if they are constantly wet, causing the structure to sag and fail.
A valley is a line formed by two pitched roofs that connect to form a V-shaped surface when viewed from the bottom. You can see an example of a roof valley in the image on the right.
A ridge is a roof peak where the two roof planes meet. You can see a ridge in a gable or hip roof. You can see an example of a roof ridge in the image on the right.
A hip is where two roof faces meet and look protruding outwards. On this meeting line, specific shingles are also known as hip and ridge shingles to cover the hip. You can see an example of a roof hip in the image on the right.
In this module, you’ve learned about the following:
The function of a roof,
Components of the roof,
Purpose of each component on the roof, and
Terms used in Roofing.
Question #1: Which of these includes a roof? (Select all that apply)
Structure
Walls
Support
Material
Scroll down for the answer...

Answer: Structure, Support and Material
Walls are different structures and aren't considered under the roof.
Question #2: Sod roofs provided excellent insulation but were ______.
Waterproof
Leaky
Sturdy
Inefficient
Scroll down for the answer...

Answer: Leaky
Sod Roofs were made of soil and plants. So, the rainwater leaked through the roof.
Question #3: Match the regions with the materials used to make roofs.
The southern part of North America - Wood and Metal
Northeast - Slate
Midwest - Wood
The southwestern part of North America - Tile
Scroll down for the answer...

Answer: The southern part of North America - Wood and Metal
Northeast - Slate
Midwest - Wood
The southwestern part of North America - Tile
The regions use the following materials:
The southern part of North America - Wood and Metal
Northeast - Slate
Midwest - Wood
The southwestern part of North America - Tile
Question #4: A flat roof is mainly installed in ________ properties_____.
Residential
Commercial
Industrial
Both B and C
Scroll down for the answer...

Answer: Both B and C
A flat roof is mainly installed in commercial or industrial properties.
Question #5: A roof keeps the house ______ in winter and ______ in summer.
warm; warm
cool; cool
cool; warm
warm; cool
Scroll down for the answer...

Answer: warm; cool
A roof keeps the house warm in winter and cool in summer.
Question #6: Why is a metal roof beneficial in snowy regions? (Select all that apply)
The roof's surface is not smooth enough to slide the snow down
The roof's surface allows it to slide the snow
The roof does not make a lot of noise during rainfall
The roof is strong enough to bear the weight of the snow.
Scroll down for the answer...

Answer: The roof's surface allows it to slide the snow and The roof is strong enough to bear the weight of the snow.
Metal roofs are beneficial in snowy regions because they are strong and can slide the snow down easily.
Other References: